Bunions Cause And Effect
Overview
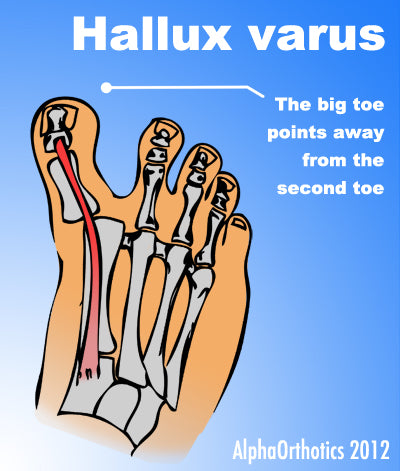 Even though bunions are a common foot deformity, there are misconceptions about them. Many people may unnecessarily suffer the pain of bunions for years before seeking treatment. A bunion (also referred to as hallux valgus or hallux abducto valgus) is often described as a bump on the side of the big toe. But a bunion is more than that. The visible bump actually reflects changes in the bony framework of the front part of the foot. The big toe leans toward the second toe, rather than pointing straight ahead. This throws the bones out of alignment, producing the bunion?s ?bump.? Bunions are a progressive disorder. They begin with a leaning of the big toe, gradually changing the angle of the bones over the years and slowly producing the characteristic bump, which becomes increasingly prominent. Symptoms usually appear at later stages, although some people never have symptoms.
Even though bunions are a common foot deformity, there are misconceptions about them. Many people may unnecessarily suffer the pain of bunions for years before seeking treatment. A bunion (also referred to as hallux valgus or hallux abducto valgus) is often described as a bump on the side of the big toe. But a bunion is more than that. The visible bump actually reflects changes in the bony framework of the front part of the foot. The big toe leans toward the second toe, rather than pointing straight ahead. This throws the bones out of alignment, producing the bunion?s ?bump.? Bunions are a progressive disorder. They begin with a leaning of the big toe, gradually changing the angle of the bones over the years and slowly producing the characteristic bump, which becomes increasingly prominent. Symptoms usually appear at later stages, although some people never have symptoms.
Causes
Long periods of pressure from a tight-fitting shoe can cause the inflammation and the pain. This often happens when the big toe is forced into a position where it presses inward and overlaps the second toe. The base of the big toe then is pushed beyond normal alignment of the foot, resulting in the prominence typical of a bunion.
Symptoms
The major symptom of bunions is a hard bump on the outside edge of the foot or at the base of the big toe. Redness, pain and swelling surrounding or at the MTP joint can also occur.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis begins with a careful history and physical examination by your doctor. This will usually include a discussion about shoe wear and the importance of shoes in the development and treatment of the condition. X-rays will probably be suggested. This allows your doctor to measure several important angles made by the bones of the feet to help determine the appropriate treatment.
Non Surgical Treatment
Wide shoes with plenty of space for the toes are the first place to start. Along these lines, a shoe can be focally stretched directly over the painful bunion using a device known as a ?ball and ring? shoe stretcher. Additionally, numerous commercial bunion braces and splints are available to help keep the big toe in better alignment. 
Surgical Treatment
There are many different procedures that have been described to correct bunions. The type of operation your foot surgeon recommends to correct your bunion should be dictated by the severity of your bunion deformity and the surgeon?s preference. There are well over 100 different bunion correction procedures described in the orthopaedic literature. However, the broad categories of bunion correction procedures are listed below. Removal of the medial eminence. Distal metatarsal osteotomy (chevron) with great toe soft-tissue tightening (medial capsular tightening and distal soft-tissue repair). Proximal metatarsal osteotomy Ludloff, Cresentic, SCARF, medial opening wedge) with with great toe soft-tissue tightening (medial capsular tightening and distal soft-tissue repair). Lapidus hallux valgus correction (first tarsometatarsal joint fusion) with distal soft tissue procedure. Great Toe Fusion (1st MTP joint arthrodesis). Akin osteotomy (Realignment bone cut at the base of the big toe). Removal of the medial eminence with suture stabilization of the first and second metatarsals. Keller joint arthroplasty (removal of the proximal aspect of the proximal phalanx).
Prevention
The best way to reduce your chances of developing bunions is to wear shoes that fit properly. Shoes that are too tight or have high heels can force your toes together. Bunions are rare in populations that don?t wear shoes. Make sure your shoes are the correct size and that there's enough room to move your toes freely. It's best to avoid wearing shoes with high heels or pointy toes.
Is Overpronation
The problem with pronation is when it is excessive, here the term overpronation (or hyper-pronation) is used. This is quite a common problem and can lead to a number of injuries, especially in runners, including shin splints, anterior compartment syndrome, patello-femoral pain syndrome, plantar fasciitis, tarsal tunnel syndrome, bunions (Hallux valgus) and achilles tendonitis.
Causes
Congenital "Flat Feet" - an individual may be born with feet that lack an appropriately supportive arch thereby predisposing the individual to this foot condition. Excessive Weight (Obesity) Too much weight on the foot from either obesity or pregnancy may be a factor. Repetitive Impact walking on flat, hard surfaces continuously places unnatural stress on the foot arch.
Symptoms
Common conditions that develop with prolonged overpronation typically include plantar fasciitis, achilles tendonitis, shin splints, posterior tibial stress syndrome and even IT band syndrome. With long term neglect you may see the development of bunyons, foot deformities and early onset of hip and knee arthritis.
Diagnosis
Do the wet foot test. Get your feet wet and walk along a paved surface or sand and look at the footprints you leave. If you have neutral feet you will see a print of the heel with a thin strip connecting to your forefoot, but if you're overpronating your foot print will look a bit like a giant blob with toes.

Non Surgical Treatment
Fortunately, there are simple things you can do to cure and correct your overpronation issues. Certain exercises help. Pull your toes back using a rolled up towel. Roll your feet over a golf or tennis ball for a minute. And do calf raises by standing up and lifting up on your toes. These all help reposition the foot and strengthen the muscles and tendons necessary for proper support. Beyond that, simple adjustments to footwear will help immensely.
Prevention
Custom-made orthotics will reduce the twisting of the leg muscles as they enter the foot, by maintaining a normal alignment of the bones and joints of the foot. If the bones and joints are aligned properly, by reducing the pronation, the muscles can run straight to their attachments in the foot, without twisting to get to these bones. This action of custom-made orthotics will reduce Achilles Tendonitis shin splints; ankle, knee, hip, and lower back pain; and leg cramps. This action will also allow the leg muscles to work more efficiently, thus allowing you to walk and run with less effort.
Calcaneal Apophysitis In Adults
Severs Disease, otherwise known as Osteochondroses, is the most common injury of its kind to affect children?s feet. The condition predominately affects children between the ages of 8 - 15 and causes pain at the back of the heel where the Achilles tendon inserts onto the bone. Children will complain of pain during activity and may have difficulty walking.
Causes
A big tendon called the Achilles tendon joins the calf muscle at the back of the leg to the heel. Sever?s disease is thought to occur because of a mismatch in growth of the calf bones to the calf muscle and Achilles tendon. If the bones grow faster than the muscles, the Achilles tendon that attaches the muscle to the heel gets tight. At the same time, until the cartilage of the calcaneum is ossified (turned into bone), it is a potential weak spot. The tight calf muscle and Achilles tendon cause a traction injury on this weak spot, resulting in inflammation and pain. Sever?s disease most commonly affects boys aged ten to 12 years and girls aged nine to 11 years, when growth spurts are beginning. Sever?s disease heals itself with time, so it is known as self-limiting. There is no evidence to suggest that Sever?s disease causes any long term problems or complications.
Symptoms
This syndrome can occur unilaterally or bilaterally. The incidence of bilaterally is approximately 60%. Common signs and symptoms include posterior inferior heel pain (over the medial and lateral surface of the bone). Pain is usually absent when the child gets up in the morning. Increased pain with weight bearing, running or jumping (= activity-related pain). The area often feels stiff. The child may limp at the end of physical activity. Tenderness at the insertion of the tendons (= an avascular necrosis of the arthropathy). Limited ankle dorsiflexion range secondary to tightness of the Achilles tendon. Hard surfaces and poor-quality or worn-out athletic shoes contribute to increased symptoms. The pain gradually resolves with rest. Reliability or validity of methods used to obtain the ankle joint dorsiflexion or biomechanical malalignment data are not commented upon, thus reducing the quality of the data. Although pain and limping are mentioned as symptomatic traits, there have been no attempts to quantify the pain or its effect on the individual.
Diagnosis
A doctor or other health professional such as a physiotherapist can diagnose Sever?s disease by asking the young person to describe their symptoms and by conducting a physical examination. In some instances, an x-ray may be necessary to rule out other causes of heel pain, such as heel fractures. Sever?s disease does not show on an x-ray because the damage is in the cartilage.
Non Surgical Treatment
The primary method of treating Sever?s disease is taking time off from sports and other physical activities to alleviate the pressure on the heel bone. During the healing period, your child?s doctor may also recommend physical therapy or any type of exercise that involves stretching and strengthen leg muscles and tendons. Wrapping ice in a towel and placing it under the child?s heel will also help to alleviate and reduce pain and swelling.
Exercise
The following exercises are commonly prescribed to patients with Severs disease. You should discuss the suitability of these exercises with your physiotherapist prior to beginning them. Generally, they should be performed 1 - 3 times daily and only provided they do not cause or increase symptoms. Your physiotherapist can advise when it is appropriate to begin the initial exercises and eventually progress to the intermediate, advanced and other exercises. As a general rule, addition of exercises or progression to more advanced exercises should take place provided there is no increase in symptoms. Calf Stretch with Towel. Begin this stretch in long sitting with your leg to be stretched in front of you. Your knee and back should be straight and a towel or rigid band placed around your foot as demonstrated. Using your foot, ankle and the towel, bring your toes towards your head as far as you can go without pain and provided you feel no more than a mild to moderate stretch in the back of your calf, Achilles tendon or leg. Hold for 5 seconds and repeat 10 times at a mild to moderate stretch provided the exercise is pain free. Calf Stretch with Towel. Begin this exercise with a resistance band around your foot and your foot and ankle held up towards your head. Slowly move your foot and ankle down against the resistance band as far as possible and comfortable without pain, tightening your calf muscle. Very slowly return back to the starting position. Repeat 10 - 20 times provided the exercise is pain free. Once you can perform 20 repetitions consistently without pain, the exercise can be progressed by gradually increasing the resistance of the band provided there is no increase in symptoms. Bridging. Begin this exercise lying on your back in the position demonstrated. Slowly lift your bottom pushing through your feet, until your knees, hips and shoulders are in a straight line. Tighten your bottom muscles (gluteals) as you do this. Hold for 2 seconds then slowly lower your bottom back down. Repeat 10 times provided the exercise is pain free.
What Causes Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction ?
Overview
Adult acquired flatfoot is a progressive disorder that involves a compromise of soft tissue supports of the medial arch. The condition most commonly affects middle aged women and is characterized by lowering of the arch, turning out of the forefoot, and a sideways angulation of the heel. There are five stages of the disorder that becomes progressively disabling. The end stage can potentially compromise the ankle joint along with the joints in the hindfoot. 
Causes
Rheumatoid arthritis This type of arthritis attacks the cartilage in the foot, leading to pain and flat feet. It is caused by auto-immune disease, where the body?s immune system attacks its own tissues. Diabetes. Having diabetes can cause nerve damage and affect the feeling in your feet and cause arch collapse. Bones can also fracture but some patients may not feel any pain due to the nerve damage. Obesity and/or hypertension (high blood pressure) This increases your risk of tendon damage and resulting flat foot.
Symptoms
Posterior tibial tendon insufficiency is divided into stages by most foot and ankle specialists. In stage I, there is pain along the posterior tibial tendon without deformity or collapse of the arch. The patient has the somewhat flat or normal-appearing foot they have always had. In stage II, deformity from the condition has started to occur, resulting in some collapse of the arch, which may or may not be noticeable. The patient may feel it as a weakness in the arch. Many patients initially present in stage II, as the ligament failure can occur at the same time as the tendon failure and therefore deformity can already be occurring as the tendon is becoming symptomatic. In stage III, the deformity has progressed to the extent where the foot becomes fixed (rigid) in its deformed position. Finally, in stage IV, deformity occurs at the ankle in addition to the deformity in the foot.
Diagnosis
There are four stages of adult-acquired flatfoot deformity (AAFD). The severity of the deformity determines your stage. For example, Stage I means there is a flatfoot position but without deformity. Pain and swelling from tendinitis is common in this stage. Stage II there is a change in the foot alignment. This means a deformity is starting to develop. The physician can still move the bones back into place manually (passively). Stage III adult-acquired flatfoot deformity (AAFD) tells us there is a fixed deformity. This means the ankle is stiff or rigid and doesn???t move beyond a neutral (midline) position. Stage IV is characterized by deformity in the foot and the ankle. The deformity may be flexible or fixed. The joints often show signs of degenerative joint disease (arthritis).
Non surgical Treatment
Stage one deformities usually respond to conservative or non-surgical therapy such as anti-inflammatory medication, casting, functional orthotics or a foot ankle orthosis called a Richie Brace. If these modalities are unsuccessful surgery is warranted. 
Surgical Treatment
Stage two deformities are less responsive to conservative therapies that can be effective in mild deformities. Bone procedures are necessary at this stage in order to recreate the arch and stabilize the foot. These procedures include isolated fusion procedures, bone grafts, and/or the repositioning of bones through cuts called osteotomies. The realigned bones are generally held in place with screws, pins, plates, or staples while the bone heals. A tendon transfer may or may not be utilized depending on the condition of the posterior tibial tendon. Stage three deformities are better treated with surgical correction, in healthy patients. Patients that are unable to tolerate surgery or the prolonged healing period are better served with either arch supports known as orthotics or bracing such as the Richie Brace. Surgical correction at this stage usually requires fusion procedures such as a triple or double arthrodesis. This involves fusing the two or three major bones in the back of the foot together with screws or pins. The most common joints fused together are the subtalar joint, talonavicular joint, and the calcaneocuboid joint. By fusing the bones together the surgeon is able to correct structural deformity and alleviate arthritic pain. Tendon transfer procedures are usually not beneficial at this stage. Stage four deformities are treated similarly but with the addition of fusing the ankle joint.
Pain Arch Foot After Running
The most common cause of arch and heel pain is a condition called plantar fasciitis. This is an inflammation of a thick band of tissue that runs along the arch of your feet from your heel to your toes, and aids in the stabilization of your arch during walking and running. Symptoms involve two areas-the arch, and more commonly, the inside heel area. Severe pain can be present, especially in the morning on arising.
Causes
In most cases, plantar fasciitis develops without a specific, identifiable reason. There are, however, many factors that can make you more prone to the condition. Tighter calf muscles that make it difficult to flex your foot and bring your toes up toward your shin. Obesity. Very high arch. Repetitive impact activity (running/sports). New or increased activity.Although many people with plantar fasciitis have heel spurs, spurs are not the cause of plantar fasciitis pain. One out of 10 people has heel spurs, but only 1 out of 20 people (5%) with heel spurs has foot pain. Because the spur is not the cause of plantar fasciitis, the pain can be treated without removing the spur.
Symptoms
Go to a podiatrist at the first sign of symptoms. Besides pain on the bottom of the foot, additional symptoms may include burning sensation in arch, difficulty standing on tiptoes, inflammation, more pain after sleeping or resting, redness, heat, localized pain in the ball of the foot, sharp or shooting pain in the toes, pain that increases when toes are flexed, tingling or numbness in the toes, aching, pain that increases when walking barefoot, pain that increases when walking on hard surfaces, pain the increases when standing (putting weight on your feet) or moving around and decreases when immobile, skin Lesions, it?s important to get a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. Let?s go over the possible causes of the pain.
Diagnosis
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) can show tendon injury and inflammation but cannot be relied on with 100% accuracy and confidence. The technique and skill of the radiologist in properly positioning the foot with the MRI beam are critical in demonstrating the sometimes obscure findings of tendon injury around the ankle. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is expensive and is not necessary in most cases to diagnose posterior tibial tendon injury. Ultrasound has also been used in some cases to diagnose tendon injury, but this test again is usually not required to make the initial diagnosis.
Non Surgical Treatment
Stretch the fascia. Prop your toes up against a wall, keeping your arch and heel flat so the toes stretch. Hold for a count of 10. Repeat 10 times three or four times per day. Roll a frozen water bottle under the arch. Stretch first then roll out the arch for 10 minutes; you don?t want to stretch the tendon when it?s ice cold. Freeze a golf ball and massage the fascia. Roll the frozen golf ball under the foot, starting from the front and working your way back. Put good pressure on each spot-the medial, center and lateral positions-for 15 seconds before moving to the next area. Then, roll the ball back and forth over the entire foot. Foam roll all muscles on the body above the plantar. Even tight shoulders can cause the condition, as your arm swing can throw off proper hip alignment and footstrike. Bump your arch. Get a commercial insole with an arch bump to push on the plantar and keep it from flexing-it doesn?t matter if you?re an under or overpronator; the plantar needs to be supported and strengthened, Wear the support in all shoes, if possible.

Surgical Treatment
Although most patients with plantar fasciitis respond to non- surgical treatment, a small percentage of patients may require surgery. If, after several months of non-surgical treatment, you continue to have heel pain, surgery will be considered. Your foot and ankle surgeon will discuss the surgical options with you and determine which approach would be most beneficial. No matter what kind of treatment you undergo for plantar fasciitis, the underlying causes that led to this condition may remain. Therefore, you will need to continue with preventive measures. Wearing supportive shoes, stretching, and using custom orthotic devices are the mainstays of long-term treatment for plantar fasciitis.
Stretching Exercises
Achilles stretch. Stand with the ball of one foot on a stair. Reach for the step below with your heel until you feel a stretch in the arch of your foot. Hold this position for 15 to 30 seconds and then relax. Repeat 3 times. Balance and reach exercises. Stand next to a chair with your injured leg farther from the chair. The chair will provide support if you need it. Stand on the foot of your injured leg and bend your knee slightly. Try to raise the arch of this foot while keeping your big toe on the floor. Keep your foot in this position. With the hand that is farther away from the chair, reach forward in front of you by bending at the waist. Avoid bending your knee any more as you do this. Repeat this 15 times. To make the exercise more challenging, reach farther in front of you. Do 2 sets of 15. While keeping your arch raised, reach the hand that is farther away from the chair across your body toward the chair. The farther you reach, the more challenging the exercise. Do 2 sets of 15. Towel pickup. With your heel on the ground, pick up a towel with your toes. Release. Repeat 10 to 20 times. When this gets easy, add more resistance by placing a book or small weight on the towel. Resisted ankle plantar flexion. Sit with your injured leg stretched out in front of you. Loop the tubing around the ball of your foot. Hold the ends of the tubing with both hands. Gently press the ball of your foot down and point your toes, stretching the tubing. Return to the starting position. Do 2 sets of 15. Resisted ankle dorsiflexion. Tie a knot in one end of the elastic tubing and shut the knot in a door. Tie a loop in the other end of the tubing and put the foot on your injured side through the loop so that the tubing goes around the top of the foot. Sit facing the door with your injured leg straight out in front of you. Move away from the door until there is tension in the tubing. Keeping your leg straight, pull the top of your foot toward your body, stretching the tubing. Slowly return to the starting position. Do 2 sets of 15. Heel raise. Stand behind a chair or counter with both feet flat on the floor. Using the chair or counter as a support, rise up onto your toes and hold for 5 seconds. Then slowly lower yourself down without holding onto the support. (It's OK to keep holding onto the support if you need to.) When this exercise becomes less painful, try doing this exercise while you are standing on the injured leg only. Repeat 15 times. Do 2 sets of 15. Rest 30 seconds between sets.
Dealing With Achilles Tendon Ruptures
Overview  Rupture of the Achilles tendon is a common injury in healthy, young, active individuals. The rupture is typically spontaneous and most commonly observed in individuals in between 24-45 years of age. The majority have had no prior history of pain or previous injury to the heel. In the majority of cases, rupture of the Achilles tendon occurs just a few centimeters above the heel bone. Common causes of Achilles tendinitis or rupture include advanced age, poor conditioning, and overexertion during exercise. In most cases, the individual rapidly performs activity like running or standing on the toes, which generates intense force on the tendon, leading to rupture. Achilles tendon rupture is often described as an abrupt break with instantaneous pain that is felt in the foot or heel area. The pain may radiate along the back of the leg and is often intense. Generally, walking may be difficult and the foot may drag. Most individuals claim that they felt like they were kicked in that area or even shot at. These symptoms lead to a suspicion of rupture of the Achilles tendon. Sometimes the tendon does not fully rupture but only a partial tear develops. The partial tear can also present with pain, and if not recognized, can rapidly develop into a full-blown rupture. In the majority of cases, the Achilles tendon rupture occurs just above the heel, but it may occur anywhere along the length of the tendon. Causes The Achilles tendon can grow weak and thin with age and lack of use. Then it becomes prone to injury or rupture. Achilles tendon rupture is more common in those with preexisting tendinitis of the Achilles tendon. Certain illnesses (such as arthritis and diabetes) and medications (such as corticosteroids and some antibiotics, including quinolones such as levofloxacin [Levaquin] and ciprofloxacin [Cipro]) can also increase the risk of rupture. Rupture most commonly occurs in the middle-aged male athlete (the weekend warrior who is engaging in a pickup game of basketball, for example). Injury often occurs during recreational sports that require bursts of jumping, pivoting, and running. Most often these are tennis, racquetball, basketball, and badminton. The injury can happen in the following situations. You make a forceful push-off with your foot while your knee is straightened by the powerful thigh muscles. One example might be starting a foot race or jumping. You suddenly trip or stumble, and your foot is thrust in front to break a fall, forcefully overstretching the tendon. You fall from a significant height or abruptly step into a hole or off of a curb. Symptoms The most common symptom of Achilles tendonitis is a sudden surge of pain in the heel and back of the ankle at the point of injury which is often described as a snapping sensation in the heel. After the injury has occurred, patients then struggle or find it near impossible to bear any weight on the affected leg. Pain can often be most prominent first thing in the morning after the injury has been rested. Swelling and tenderness is also likely to appear in the area. Diagnosis If an Achilles tendon rupture is suspected, it is important to consult a doctor straight away so that an accurate diagnosis can be made and appropriate treatment recommended. Until a doctor can be consulted it is important to let the foot hang down with the toes pointed to the ground. This prevents the ends of the ruptured tendon pulling any farther apart. The doctor will take a full medical history, including any previous Achilles tendon injuries and what activity was being undertaken at the time the present injury occurred. The doctor will also conduct a physical examination and will check for swelling, tenderness and range of movement in the lower leg and foot. A noticeable gap may be able to be felt in the tendon at the site of the rupture. This is most obvious just after the rupture has occurred and swelling will eventually make this gap difficult to feel. One test commonly used to confirm an Achilles tendon rupture is the Thomson test. For this test the patient lies face down on an examination table. The doctor then squeezes the calf muscles; an action that would normally cause the foot to point like a ballerina (plantar flexion). When a partial rupture has occurred the foot's ability to point may be decreased. When a complete rupture has occurred, the foot may not point at all. Ultrasound scanning of the Achilles tendon may also be recommended in order to assist with the diagnosis. Non Surgical Treatment Once the Achilles tendon is partially damaged, one should exercise great care. The risk of rupture is high and if pain is associated with walking, one should consult with an orthopedic surgeon or a sports physician. A complete rupture of the Achilles tendon is never treated at home. It is important to understand that there are no minerals, nutrients, or herbs to treat Achilles tendon injury and any delay just worsens the recovery.
Rupture of the Achilles tendon is a common injury in healthy, young, active individuals. The rupture is typically spontaneous and most commonly observed in individuals in between 24-45 years of age. The majority have had no prior history of pain or previous injury to the heel. In the majority of cases, rupture of the Achilles tendon occurs just a few centimeters above the heel bone. Common causes of Achilles tendinitis or rupture include advanced age, poor conditioning, and overexertion during exercise. In most cases, the individual rapidly performs activity like running or standing on the toes, which generates intense force on the tendon, leading to rupture. Achilles tendon rupture is often described as an abrupt break with instantaneous pain that is felt in the foot or heel area. The pain may radiate along the back of the leg and is often intense. Generally, walking may be difficult and the foot may drag. Most individuals claim that they felt like they were kicked in that area or even shot at. These symptoms lead to a suspicion of rupture of the Achilles tendon. Sometimes the tendon does not fully rupture but only a partial tear develops. The partial tear can also present with pain, and if not recognized, can rapidly develop into a full-blown rupture. In the majority of cases, the Achilles tendon rupture occurs just above the heel, but it may occur anywhere along the length of the tendon. Causes The Achilles tendon can grow weak and thin with age and lack of use. Then it becomes prone to injury or rupture. Achilles tendon rupture is more common in those with preexisting tendinitis of the Achilles tendon. Certain illnesses (such as arthritis and diabetes) and medications (such as corticosteroids and some antibiotics, including quinolones such as levofloxacin [Levaquin] and ciprofloxacin [Cipro]) can also increase the risk of rupture. Rupture most commonly occurs in the middle-aged male athlete (the weekend warrior who is engaging in a pickup game of basketball, for example). Injury often occurs during recreational sports that require bursts of jumping, pivoting, and running. Most often these are tennis, racquetball, basketball, and badminton. The injury can happen in the following situations. You make a forceful push-off with your foot while your knee is straightened by the powerful thigh muscles. One example might be starting a foot race or jumping. You suddenly trip or stumble, and your foot is thrust in front to break a fall, forcefully overstretching the tendon. You fall from a significant height or abruptly step into a hole or off of a curb. Symptoms The most common symptom of Achilles tendonitis is a sudden surge of pain in the heel and back of the ankle at the point of injury which is often described as a snapping sensation in the heel. After the injury has occurred, patients then struggle or find it near impossible to bear any weight on the affected leg. Pain can often be most prominent first thing in the morning after the injury has been rested. Swelling and tenderness is also likely to appear in the area. Diagnosis If an Achilles tendon rupture is suspected, it is important to consult a doctor straight away so that an accurate diagnosis can be made and appropriate treatment recommended. Until a doctor can be consulted it is important to let the foot hang down with the toes pointed to the ground. This prevents the ends of the ruptured tendon pulling any farther apart. The doctor will take a full medical history, including any previous Achilles tendon injuries and what activity was being undertaken at the time the present injury occurred. The doctor will also conduct a physical examination and will check for swelling, tenderness and range of movement in the lower leg and foot. A noticeable gap may be able to be felt in the tendon at the site of the rupture. This is most obvious just after the rupture has occurred and swelling will eventually make this gap difficult to feel. One test commonly used to confirm an Achilles tendon rupture is the Thomson test. For this test the patient lies face down on an examination table. The doctor then squeezes the calf muscles; an action that would normally cause the foot to point like a ballerina (plantar flexion). When a partial rupture has occurred the foot's ability to point may be decreased. When a complete rupture has occurred, the foot may not point at all. Ultrasound scanning of the Achilles tendon may also be recommended in order to assist with the diagnosis. Non Surgical Treatment Once the Achilles tendon is partially damaged, one should exercise great care. The risk of rupture is high and if pain is associated with walking, one should consult with an orthopedic surgeon or a sports physician. A complete rupture of the Achilles tendon is never treated at home. It is important to understand that there are no minerals, nutrients, or herbs to treat Achilles tendon injury and any delay just worsens the recovery.  Surgical Treatment An Achilles tendon rupture is a complete tear of the fibrous tissue that connects the heel to the calf muscle. This is often caused by a sudden movement that overextends the tendon and usually occurs while running or playing sports such as basketball or racquetball. Achilles tendon rupture can affect anyone, but occurs most often in middle-aged men. Prevention Prevention centers on appropriate daily Achilles stretching and pre-activity warm-up. Maintain a continuous level of activity in your sport or work up gradually to full participation if you have been out of the sport for a period of time. Good overall muscle conditioning helps maintain a healthy tendon.
Surgical Treatment An Achilles tendon rupture is a complete tear of the fibrous tissue that connects the heel to the calf muscle. This is often caused by a sudden movement that overextends the tendon and usually occurs while running or playing sports such as basketball or racquetball. Achilles tendon rupture can affect anyone, but occurs most often in middle-aged men. Prevention Prevention centers on appropriate daily Achilles stretching and pre-activity warm-up. Maintain a continuous level of activity in your sport or work up gradually to full participation if you have been out of the sport for a period of time. Good overall muscle conditioning helps maintain a healthy tendon.